PermalinkAbstract
A binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree data structure, which can have a maximum of two child nodes, but with the condition that the left subtree will always have values lesser than the root node's value, and the right subtree will always have values greater than the value possessed by the root node. This makes the binary tree a very efficient data structure for performing searching operations. So, whenever you want to store data so that it becomes easy for you to search and then insert/modify data in the future, BST should be your first thought.
PermalinkScope of this article
- This article starts with the basic definition of the tree data structure and then graduates to explaining what a Binary Search Tree (BST) is.
- This article covers in detail why Binary Search Tree is better for searching operations than any other data structures such as arrays (sorted and unsorted) and Linked Lists.
- This article covers the basic operations that can be performed using Binary Search Tree with their pseudo-codes.
PermalinkContents
- What is a Tree?
- What is a Binary Tree?
- What is a Binary Search Tree?
- Why use BST?
- Operations on BST
- Why is BST best for searching?
- Searching in Arrays (Sorted)
- Searching in Arrays (Unsorted)
- Searching on LinkedList
- Final Time Complexity Calculation
PermalinkWhat is a Tree?
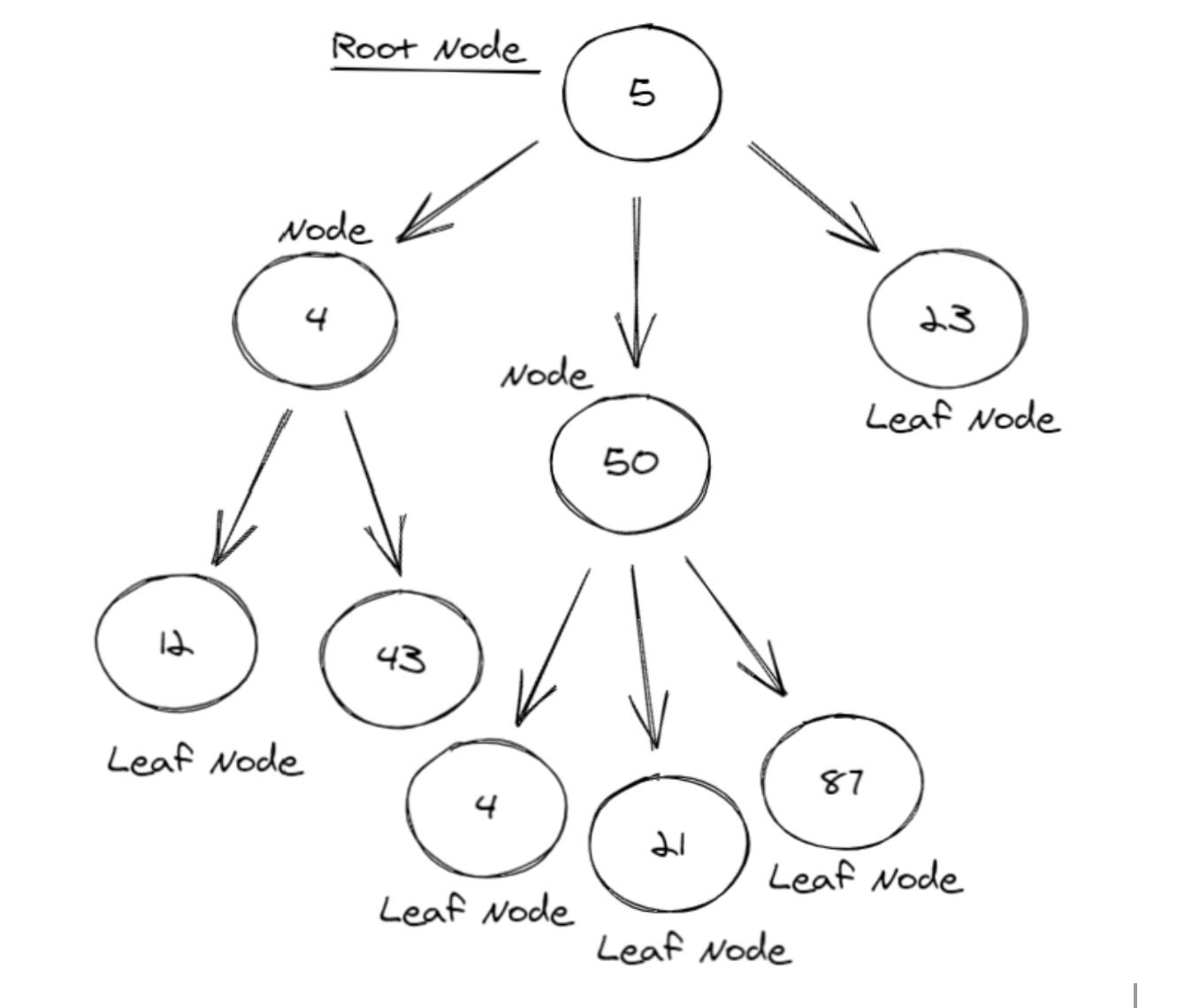
A tree is a special type of data structure that follows a hierarchical flow of data storage. In real life, a tree is made up of leaves, right? A tree here is made up of nodes. Every node can have any number of children nodes attached to it. The topmost node is called the root node, and the node with no child nodes is called a leaf node.
Each child node can either be a subtree in itself (i.e., have its own children nodes) or will be a leaf node (i.e., will have no child nodes). This is what a regular tree looks like:
PermalinkWhat is a Binary Tree?
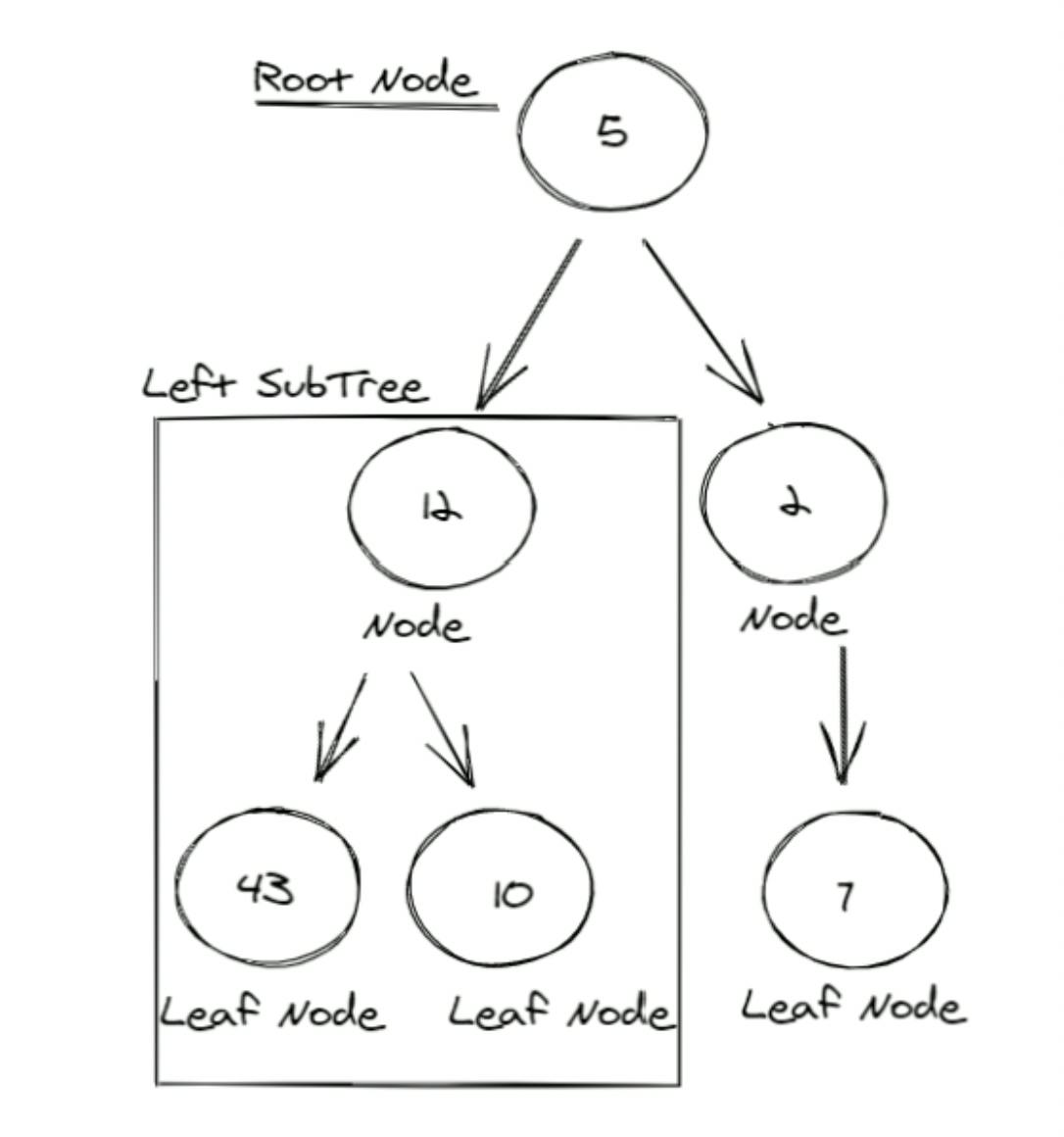
What makes a tree, a binary Tree? Binary means Two! A tree that has at most two child nodes is called a Binary Tree. That means it can have zero, one, or two children nodes. These two children nodes are called the left and the right subtrees, respectively. This is what a binary tree looks like:
PermalinkWhat is a Binary Search Tree?
Let's break the word 'Binary Search Tree' into three parts:
- Binary means the tree can have at most two children nodes/subtrees.
- Search means it follows the Binary Search strategy. a. All the nodes in the left subtree will hold values lesser than the root node's value b. All the nodes in the right subtree will have values greater than the root node's value.
- Every child subtree will also be a Binary Search Tree (BST).
PermalinkExamples:
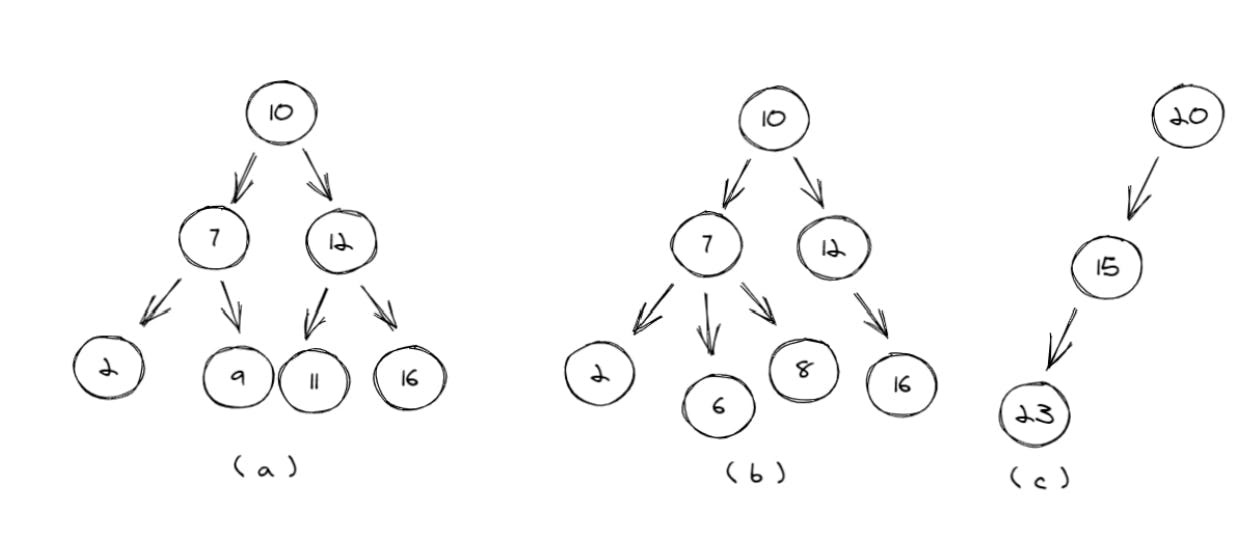
We'll discuss all three parts using these three rules:
Rule 1: Every node has at most two children nodes.
Rule 2: Every node in the left subtree has values lesser than the root node.
Rule 3: Every node in the right subtree has values greater than the root node.
Now let's discuss the examples one by one:
- In the first tree, every node has at most two children nodes, and every node in the left subtree has a value less than 10. In the left subtree, every node in the left subtree has a value less than 7. The same is true for the right subtree. Hence, this is a BST.
- In the second tree, Rule 1 does not hold. One of the nodes has more than two children nodes in their subtree. Hence, this is NOT a BST.
- The third subtree doesn't look like a BST. So, let's examine this one carefully. Rule 1 holds since every node has at most two nodes in their subtrees. Rule 2 doesn't fit well because 23 > 20 but is present in the left subtree of the root node. Hence, this is NOT a BST.
PermalinkWhy use BST?
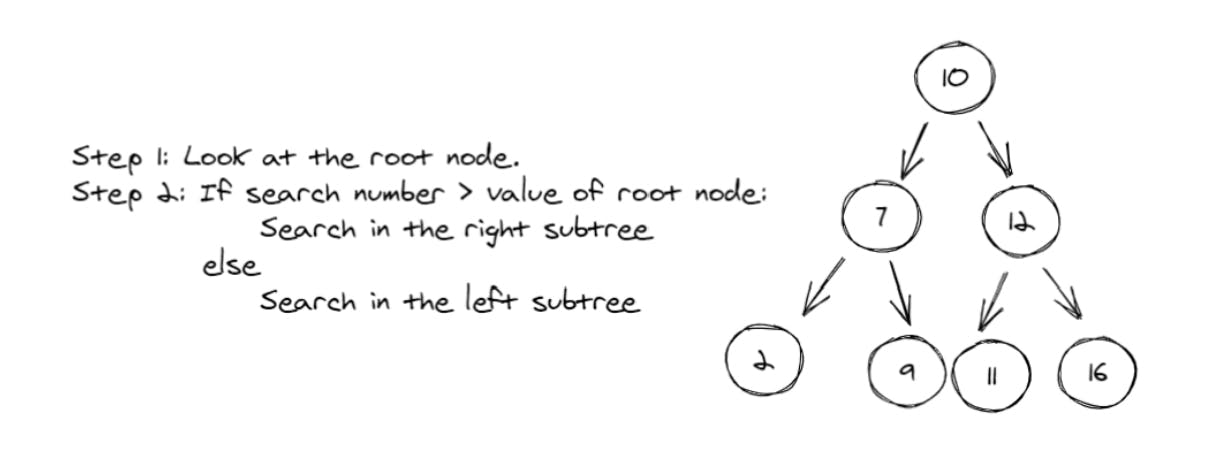
BST is the best data structure used for applications where searching is the most common operation to perform. Why? Because BST makes searching so easy. For example, if we have a BST shown below, and we want to find the number 16, we'll use the following algorithm:
PermalinkOperations on Binary Search Tree
Searching in a Binary Search Tree

Insertion in a Binary Search Tree
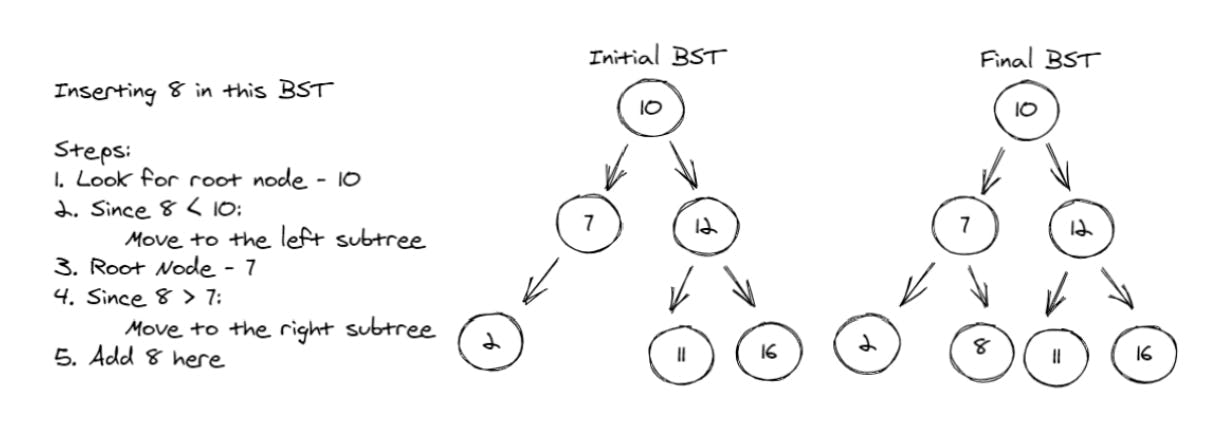
PermalinkWhy is BST best for searching?
Let us consider different data structures to understand why BST is the best choice. We'll be talking about the time complexity, arrays, and linked list take for the searching and insertion operations for this task.
PermalinkTime Complexity for using (Unsorted) Arrays
An array is a linear data structure, and if we want to find an element, we'll have to traverse the whole array and look for the 'search element' one by one. This makes the search time complexity of O(n).
If we want to insert an element, we can simply insert it to the end of the array in O(1), considering the array is not completely filled. If the array is completely filled, we'll have to create a larger array and then shift all the elements to the new array, which will be O(n) time complexity. On average, the time complexity for insertion in an unsorted array is taken as O(1).

PermalinkTime Complexity for using (Sorted) Arrays
If the data is sorted inside the array, we'll use the Binary Search algorithm to search the element. This reduces the time complexity to O(log n). We use the Divide and Conquer algorithm to find the 'search element.' The array is divided into half every time, and the better half is looked for the search element. This is how it works:
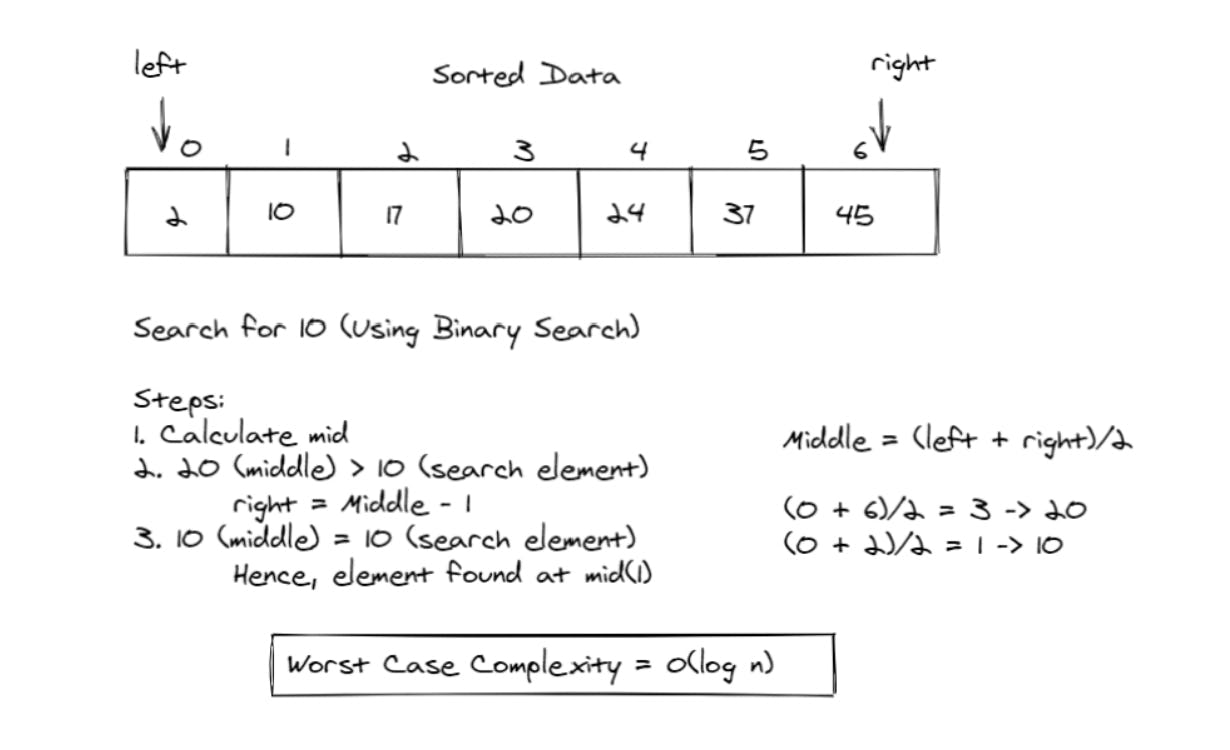
Now, if we want to insert an element inside a sorted array, we'll first have to search the right place for that element and then perform the insertion operation. We know searching takes O(log n) time complexity in a sorted array. After searching, we'll have to shift the other elements to the right and adjust this new element inside the array in a sorted manner. Hence, insertion costs O(n).
PermalinkTime Complexity for using LinkedList
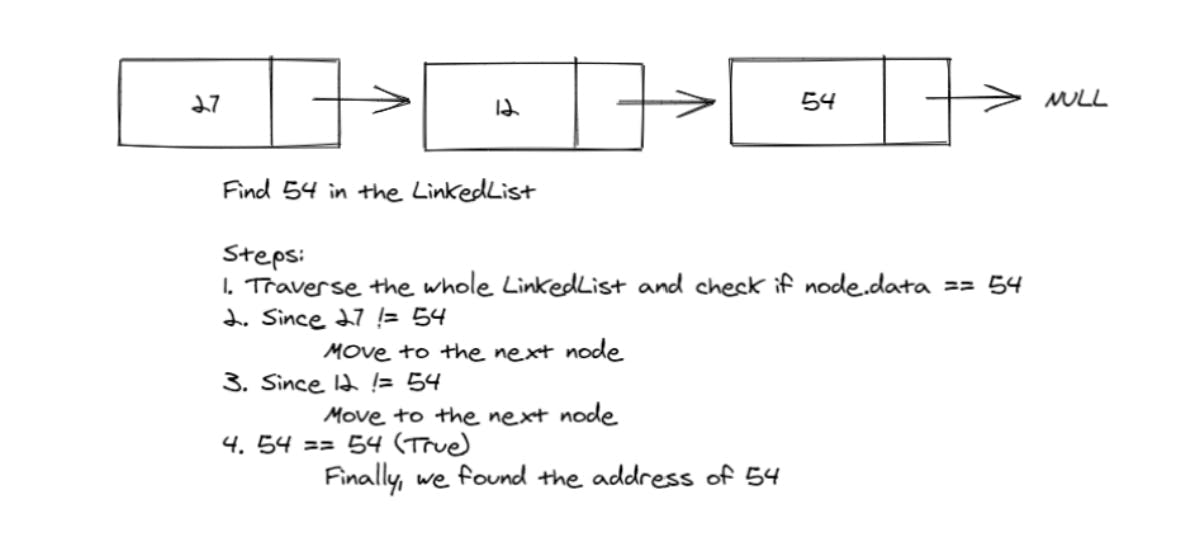
A LinkedList is a linear data structure that holds data at dynamic locations, and every node holds the address to the next node along with its own data. To search an element inside a LinkedList, we'll have to traverse the whole LinkedList in the worst case, making the time complexity for searching - O(n).
If we want to add an element to the end of the LinkedList, or at a particular position, we'll have to traverse each node one by one and then add the new node. This makes the worst-case time complexity of insertion - O(n).
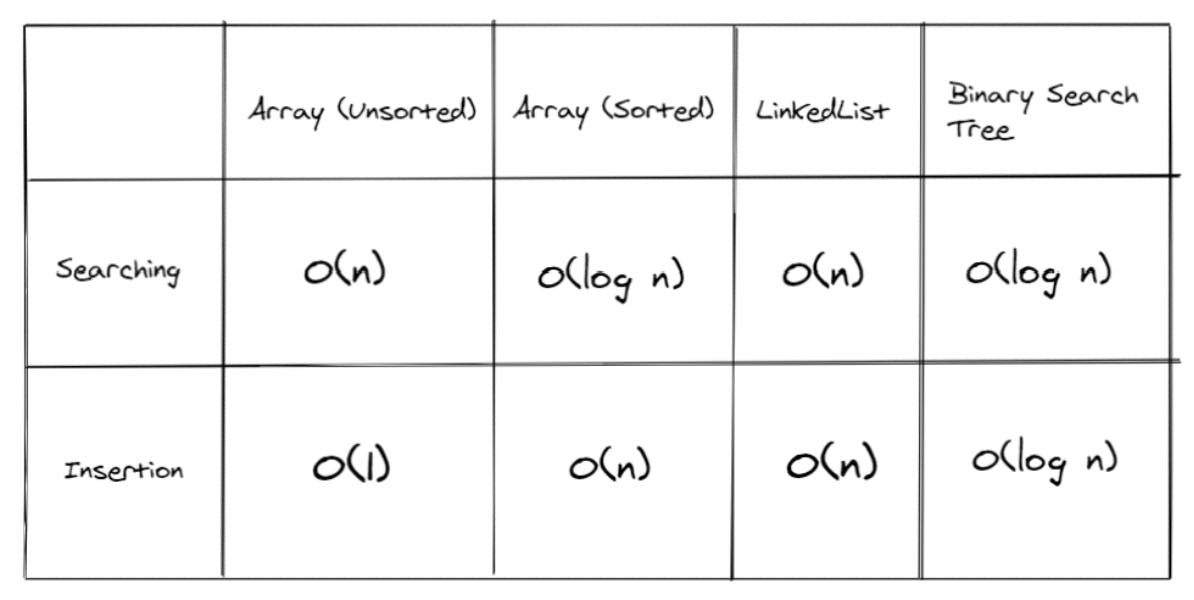
PermalinkFinal Time Complexity Analysis
PermalinkSummary
- A binary Search Tree is a very efficient data structure for organizing data in such a way that makes data modification (insertion/deletion) easier.
- While searching can be done using arrays too when it comes to a huge database, O(n) becomes a very costly time complexity.
- Hence, Binary Search Trees with the time complexity of O(log n) help search even faster and modification operations less complex.
